Combination Therapies and Synergistic Approaches
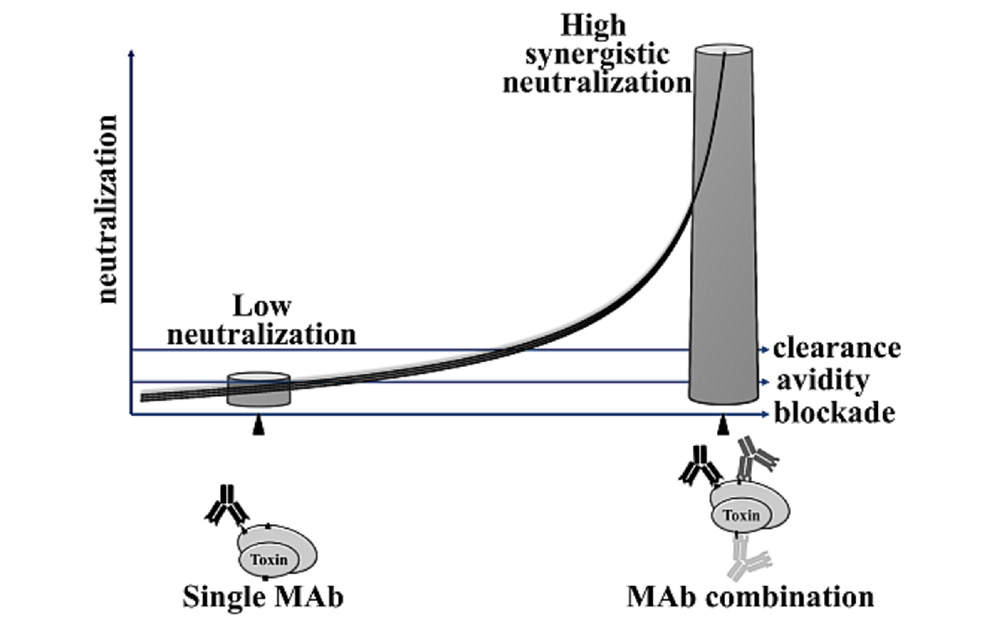
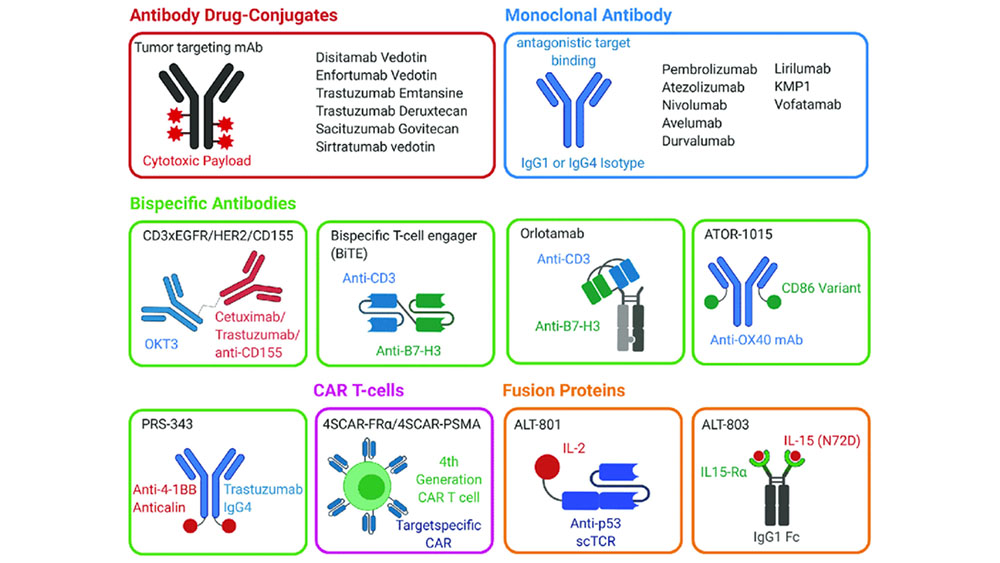
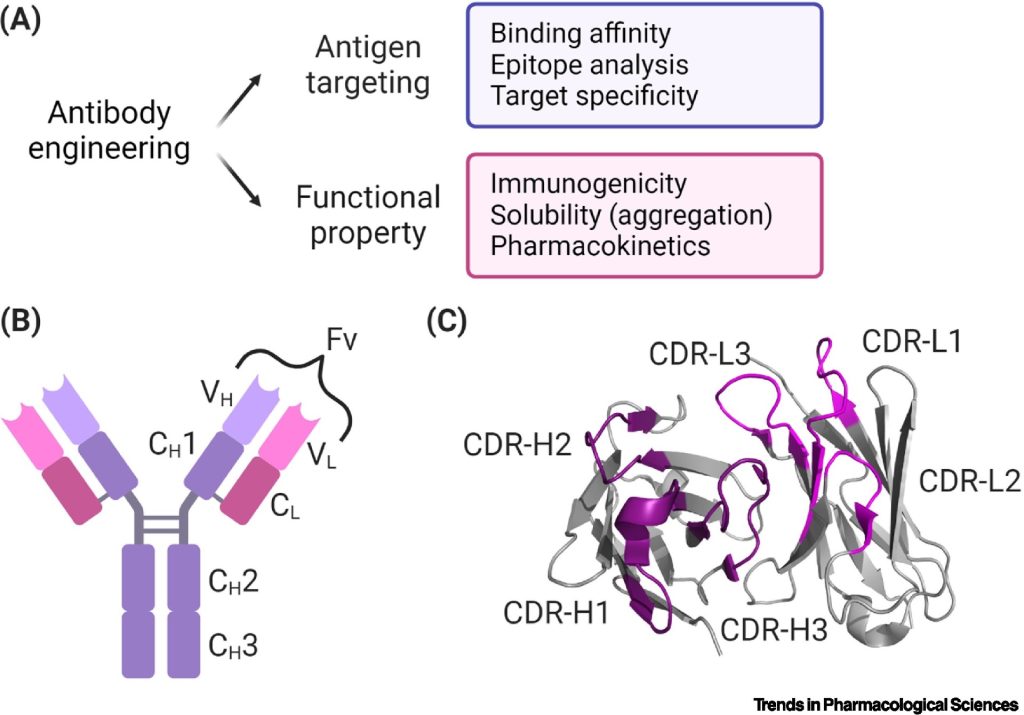
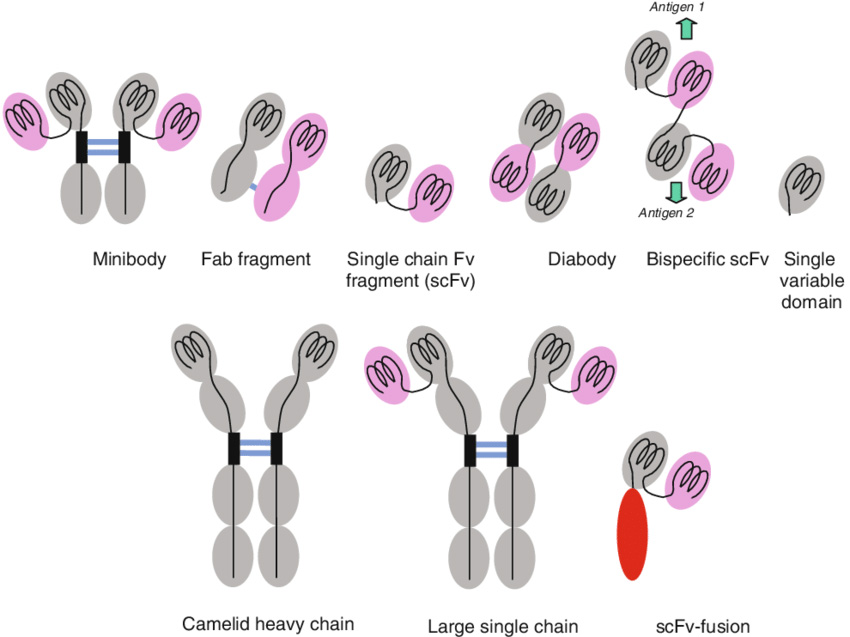
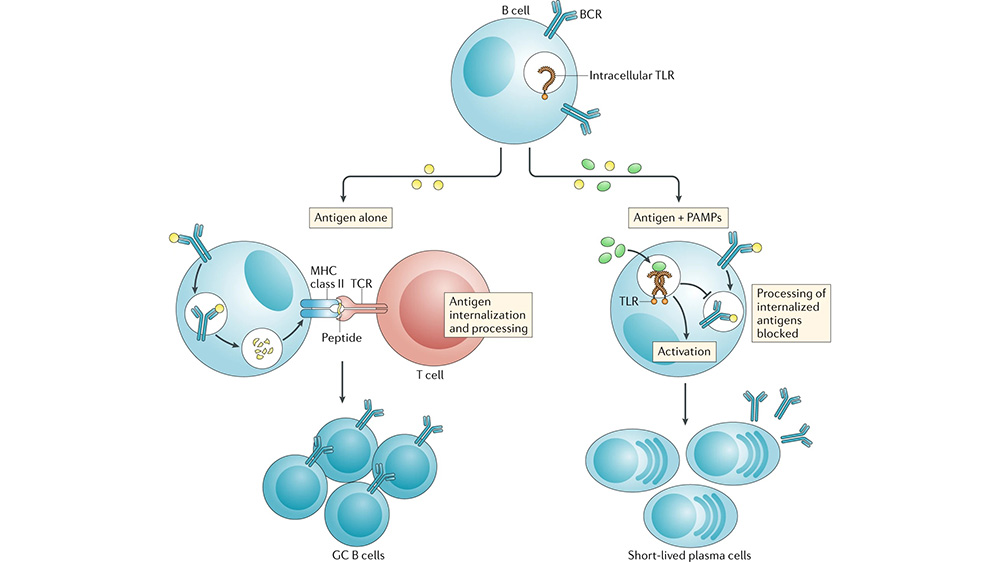
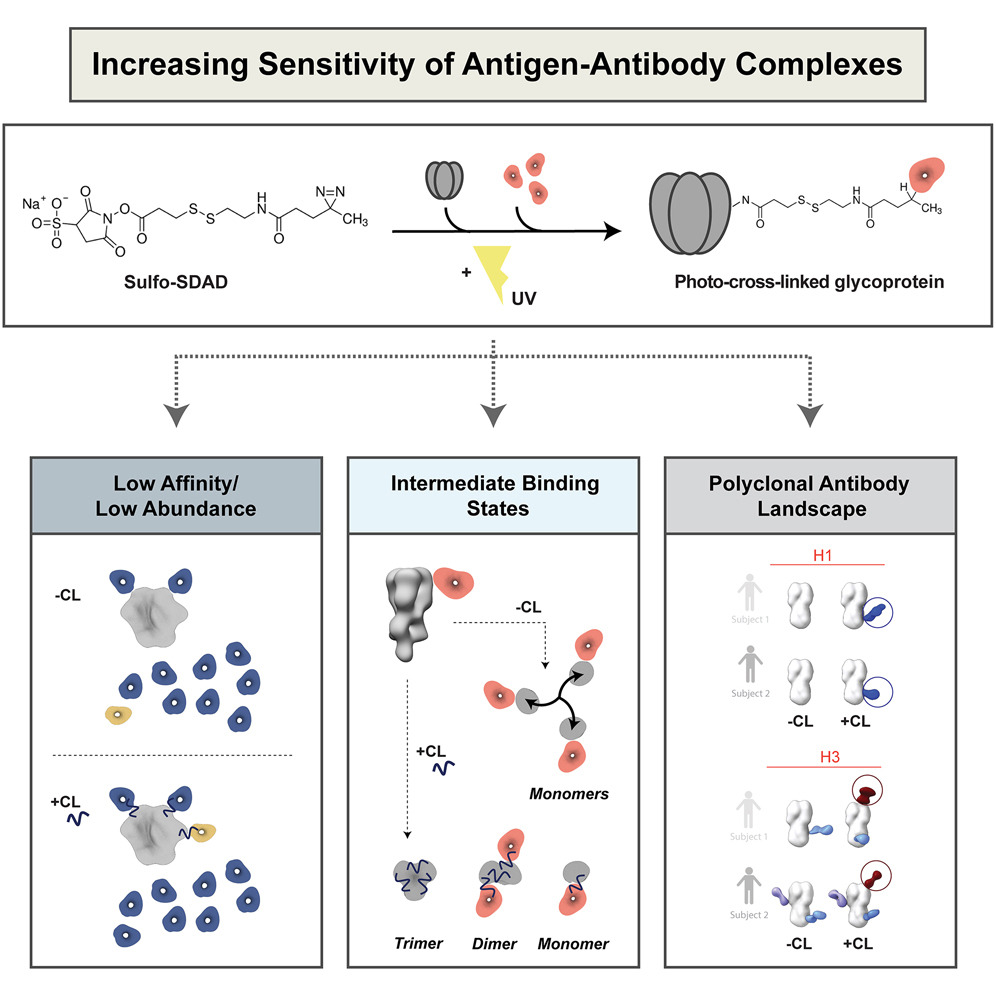
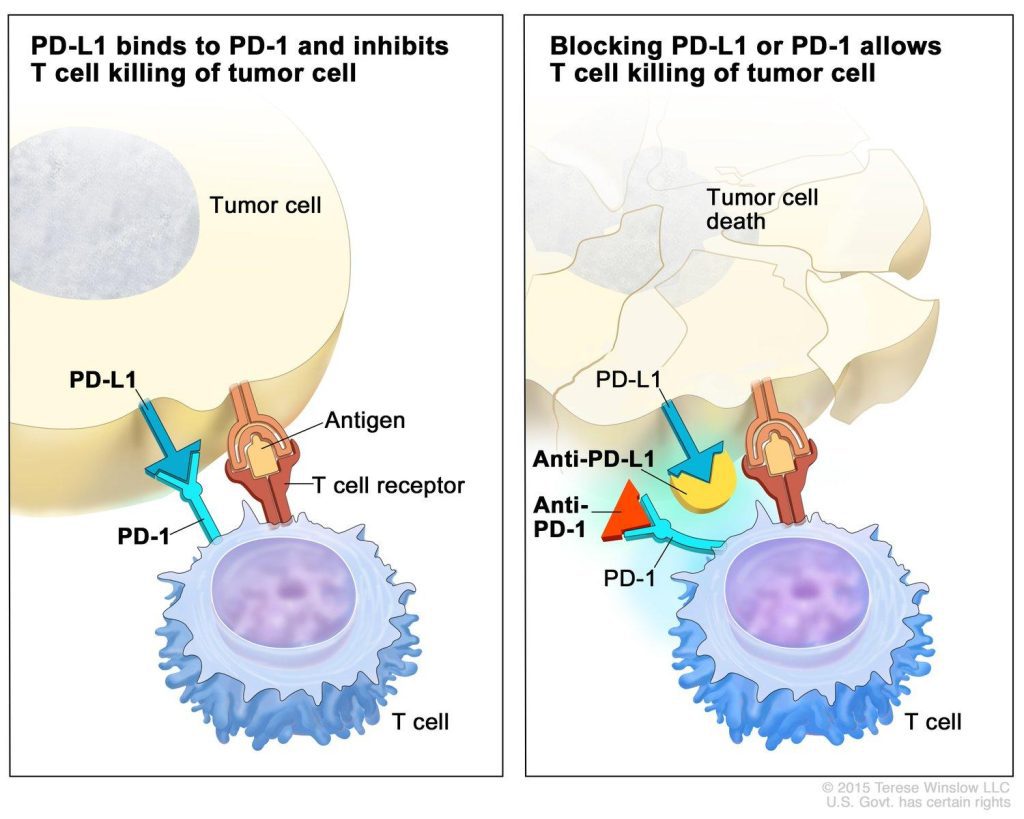
Combination therapies and synergistic approaches refer to the use of multiple treatments or interventions together to enhance their effectiveness in addressing a disease. This approach is employed in various fields of medicine, including cancer, infectious diseases, and mental health. Monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapeutics have been successfully developed and commercialized for various indications, including the neutralization […]
Combination Therapies and Synergistic Approaches Read More »